Electrochemical metal corrosion protection is one of the most appropriate protection for structures that are exposed to aggressive environments. In practice, two methods of protection are used, cathodic and anodic. What is the difference between them?
The significance of corrosion protection
Corrosion is one of the major problems facing today’s metallurgy. Aside from the impact on materials, corrosion is also a major economic problem. Through the development of science and technology, new methods of protection have been found, which are further refined every year. However, among all the methods of protection, one is considered to be the best, and that is electrochemical protection.
There are two basic methods of electrochemical protection:
- Cathodic protection
- Anodic protection
However, a few more words about electrochemical protection before the detailed explanation of these methods. The metal that is corrosion-protected through an electrochemical process, is held in a passive state. The metals that are being corrosion-protected in such a way are most often used in burial and immersion constructions.
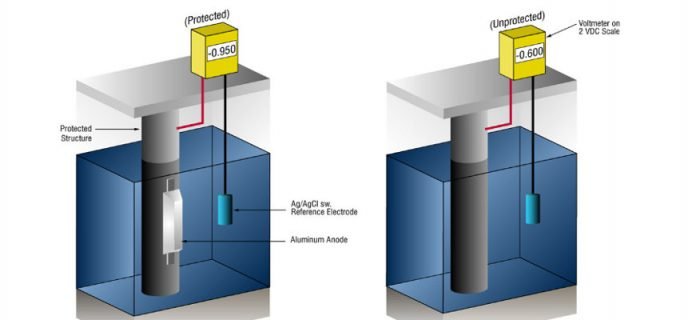
Cathodic electrochemical protection
Cathodic protection is one of the most widely used methods of electrochemical protection. There are two ways of developing this kind of protection today:
- Protection through an external current source – the metal that is to be protected is connected to the negative pole of the DC current source
- Protection with the sacrificial anode – the metal is bonded to the material that is negatively charged, after which the anodic dissolution, ie cathodic protection happens
Some of the main advantages of this type of electrochemical metal protection are:
- Simplicity
- No need for frequent controls
- No power source dependency
- It has almost no effect on structures with a structure that is protected in such a way
However, besides the positive sides, there are several negative ones as well. They are primarily related to environmental pollution, ie application in a microenvironment that has characteristic properties (eg resistance, …).
Anodic metal protection
The principle of anodic metal protection is very similar to the principle of cathodic protection. There are two basic ways of protection:
- DC Protection – The DC current has a passivating effect on the metal
- Protector protection – protection is achieved in a way that the metal which is to be protected is connected to the protector that is generally positively charged
Anodic electrochemical protection has a much smaller application in practice compared to cathodic protection. For example, anodic protection is most often used for the passivation of steel, inox, aluminum, chromium, and titanium or their alloys. One of the most common applications of anodic corrosion protection is the protection of steel in an aggressive environment in which acids are prevalent.
Electrochemical metal protection in practice
Electrochemical metal protection is most commonly encountered, as mentioned above, in constructions that are immersed in water. It is worth mentioning the practice of cathodic protection of some parts of the ship that are constantly immersed in water. Thus, for example on the parts of the rudder or on the hull of the ship, the protectors that together with the DC current protect the hull from possible corrosion, are placed.