Safety Guidelines to Follow when Laser Marking
Safety guidelines allow you to control laser beams and prevent the occurrence of hazards and injuries. There are three main categories of safety guidelines you can use, discussed below:
Administrative control
This control is an important part of every business or company using a laser marker machine that allows them to protect their personnel, working space, and equipment
· Work With Trained Personnel
Unskilled operators are liable to misuse laser marking machines putting them at risk of injuries earlier discussed. Before employing an individual, ensure they have received the necessary training and instructions on laser marking.
Proper training reduces accidental exposure to laser beams. Furthermore, equipment is not damaged as skilled operators can align the laser beam and detect malfunctioning equipment early.
· Put Up a Warning Sign
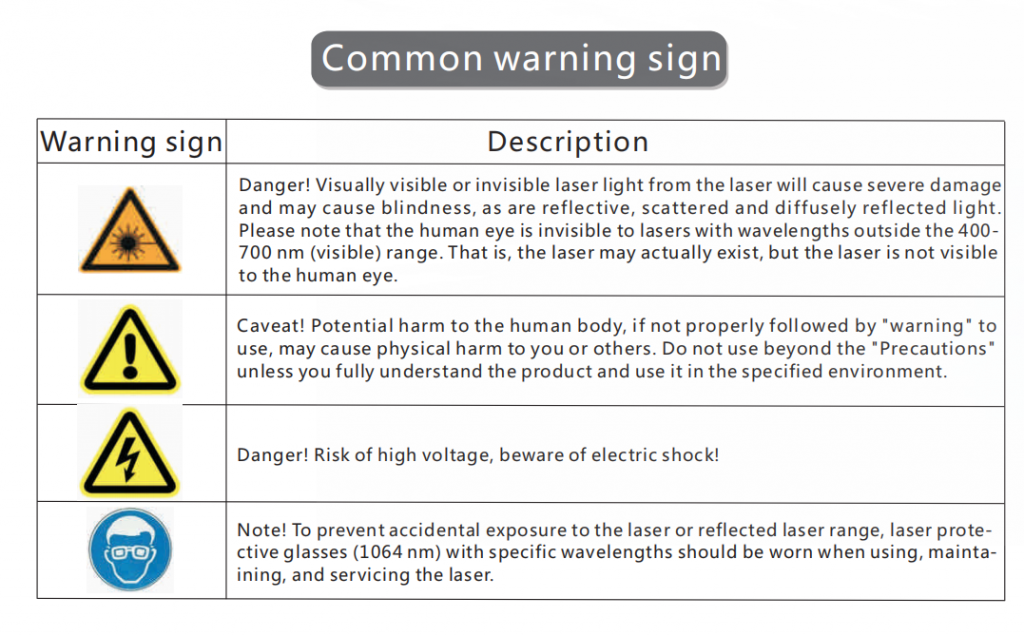 Put up a warning sign where a laser marker is being used to ensure that employees and visitors are aware of the risks. The sign should also include certain types of reflective clothing operators should not wear.
Put up a warning sign where a laser marker is being used to ensure that employees and visitors are aware of the risks. The sign should also include certain types of reflective clothing operators should not wear.
· Proper Usage and Maintenance of the Laser Marking Machine
To prevent accidents, install modules that allow proper use and maintenance of laser marking machines. For example, ensure sufficient ventilation to prevent fire outbreaks—properly removing residues and debris for a clean environment and marking processes. Furthermore, the use of exhausting fume systems to remove the generation of fumes and the use of fire extinguishers in cases of a fire outbreak.
· Use Only Approved Materials
Some materials emit hazardous and corrosive fumes during marking, putting the operator and other employees at risk. As a result, businesses should only mark compatible materials.
Operator control
The control here contains safety guidelines targeted at the personnel and equipment.
· Protective Enclosure
Protective enclosures are an effective way of controlling and preventing laser marking hazards and injuries. They function by enclosing the machine and the part from the environment, thereby reducing the exposure of the laser beam and lessening the risk associated with such exposure.
Create a shield around the head of the marker. Doing this protects operators and other employees from unintentional reflected light. The material used for shielding should have the appropriate heat and reflectance properties to block reflected laser light.
· Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPEs)
It may be necessary to wear PPEs when engineering control is insufficient to prevent access to direct or reflected beams at levels exceeding the maximum permissible limits. However, using PPEs as the only control measure may not be effective in using class IV lasers.
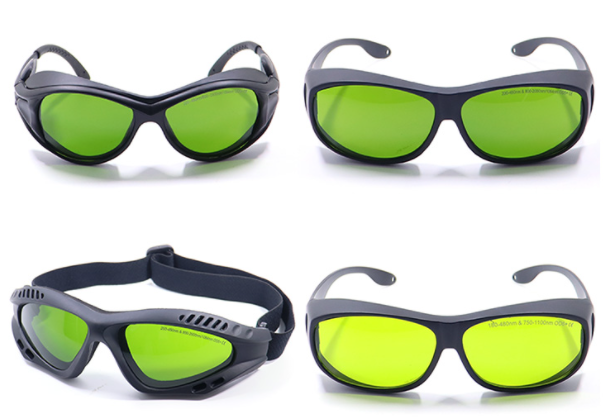
· Protective Eyewear
Protective eyewear prevents your eyes from getting irradiated with laser marking machines, especially the class III and IV lasers. Examples of protective eyewear include laser safety goggles, face shields, or eyewear with particular filter materials.
Each laser marking system has a pair of laser safety glasses specific to their wavelength. Common ones include:
- CO2 lasers with a wavelength of 10.6-micrometre work with eyeglasses with an optical density of 5-7.
- Fiber lasers with a wavelength of 1090 nanometer work with eyeglasses with an optical density of 6 and above.
Note: Operators should wear protective eyewear throughout the marking process
· Protective Bodywear
When using class IV lasers, operators must wear flame-resistant clothing and take every precaution to safeguard their skin. This is because skin burns when the body comes in contact with a laser beam. Also, puncture wounds and lacerations could result from sharp edges.
Keep the protective wear and eyewear in a separate case or storage unit to prevent scratches and contamination. Any damage can compromise the level of protection.
