

Over the past decade, System on Chips (SoCs) and System on Modules (SoMs) have gained immense popularity among engineers, receiving praise for their numerous benefits. These technologies have revolutionized hardware design, offering a more compact and efficient solution. However, as with any technological advancement, they come with their own set of challenges. To truly grasp the reasons behind the popularity of SoCs and SoMs and understand the obstacles they present, it is essential to delve into the changing landscape of hardware design and explore the potential workarounds for these issues. So, why have SoCs and SoMs become so popular, what challenges do they introduce, and how could engineers navigate these challenges?
Top Stories This Week
Hardware Business News
Netherlands’ Export Controls: Impact On Global Semiconductor Industry
Recently, the Netherlands made headlines with the announcement of new rules that will impose restrictions on exports related to semiconductor manufacturing equipment, particularly those produced by ASML, a leading manufacturer in the field. The decision to implement these restrictions came after increasing pressure from the United States. This development raises several important questions: Why is the Netherlands such a critical player in the global semiconductor manufacturing landscape, what exactly do these restrictions entail, and does this situation underscore the significant influence that the US wields over the semiconductor market?
Current Grid Networks May Not Be Able To Handle Green Revolution

Whether it’s not enough lithium or the dependence on fossil-derived fuels, there seem to be multiple factors preventing the green energy transformation that the world desperately needs. Now, a new report has shed light on the electrical grid and how it may not be suitable for future energy needs as a result of EVs and heat pumps. What challenges do these new renewable technologies introduce, what impact would this have on the electric grid, and are there alternative solutions?
China Introduces Export Controls On Gallium & Germanium Products

As the West continues to tighten controls over exports of semiconductors, China has just fired a broadside attack with its introduction of export controls over Gallium and Germanium, two critical rare-earth metals used to manufacture semiconductors. A dominant player in the global supply of these critical metals, China produces 60% of the world’s germanium and 80% of the world’s gallium. This move by China to restrict exports of these metals could have far-reaching implications for the global electronics industry. What role do these materials play in the manufacture of semiconductors, what rules have been brought forward by China, and what does this mean for the West?
The FAA Has Approved The World’s First Electric Flying Car
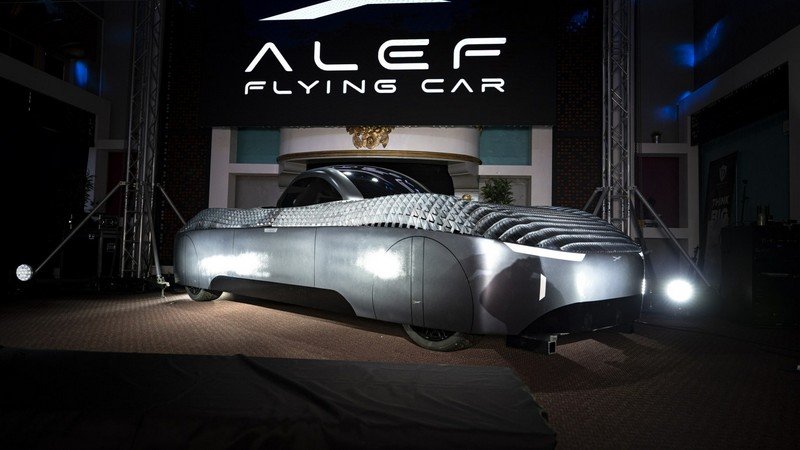

Recently, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has achieved a ground-breaking milestone by certifying the world’s first fully electric flying vehicle. Designed by Alef Aeronautics, the Model A has a driving range of up to 200 miles and a flying range of over 100 miles but while its designers are hopeful that it will become a new mode of transport, others are concerned over its safety. What impact will this ground-breaking development have on the future of personal transportation, how will the integration of eVTOL vehicles affect urban mobility, and what challenges must be overcome to ensure widespread adoption and regulatory approval for electric flying vehicles?
Hardware Engineering News
The Science Behind Self-Powered Sensors: How They Work And Why They Matter
Self-powered sensors are revolutionizing industries with their ability to generate their own power from the surrounding environment. These sensors offer a sustainable and low-maintenance solution for various applications, from healthcare to environmental monitoring. By harnessing ambient energy sources such as solar, thermal, kinetic, or radio frequency energy, self-powered sensors can operate without the need for batteries or external power supplies, making them ideal for remote locations. What impact will self-powered sensors have on healthcare and environmental monitoring, how will the reliance on ambient energy sources influence the design and deployment of sensor networks, and what challenges need to be addressed to ensure the widespread adoption of self-powered sensors?
The Future Of Fabric: Programmable Weaving Unleashes Smart Fabric Potential

Advancements in wearable technology have paved the way for the development of smart fabrics and wearable sensors, offering a range of applications in healthcare and beyond. However, the challenge of large-scale manufacturing for smart fabrics remains. A recent breakthrough may change this, as researchers have demonstrated a fully automated e-textile manufacturing process capable of creating smart fabrics with multiple types of fiber devices seamlessly integrated. This opens up possibilities for convenient health monitoring, smart environments, and more. What are the potential benefits of smart fabrics and wearable technology in terms of health monitoring and daily convenience, how does the automated e-textile manufacturing process enable the seamless integration of electronic components into fabrics, and what are some practical applications of smart fabrics in healthcare, environmental monitoring, waste management, and other fields?
The Humane AI Pin Wants To End Our Dependence On Screens

Humane, a company founded by former Apple executives, is set to launch its first product, the Humane Ai Pin, later this year. Designed to reduce dependence on smartphones, this wearable device incorporates contextually aware artificial intelligence. While specific details about the device are scarce, a recent TED Talk by Humane President Imran Chaudhri provides a glimpse into its transformative capabilities. How does the Humane Ai Pin leverage contextually aware artificial intelligence to reduce smartphone reliance, what are the potential challenges and limitations of voice-controlled wearables, such as the Ai Pin, in terms of replacing screen-based interactions, how might Humane address concerns related to privacy, translation accuracy, and the practicality of projecting detailed information using a wearable device?
Hardware R&D News
Smart Watches Could Detect Parkinson’s Seven Years Before Symptoms

Smart watches have the potential to detect Parkinson’s disease up to seven years before the onset of key symptoms, according to a recent study. Using artificial intelligence, researchers analysed the movement speed of participants wearing medical-grade smart watches over a seven-day period and accurately predicted who would develop the disease. How did the researchers use artificial intelligence and smart watches to predict the development of Parkinson’s disease, what are the potential benefits of early detection of Parkinson’s, and how could it improve patient outcomes, and what challenges and limitations exist in using smart watches as a screening tool for Parkinson’s, and how can these be addressed to ensure accuracy and reliability?
Researchers Create Highly Conductive Metallic Gel For 3D Printing
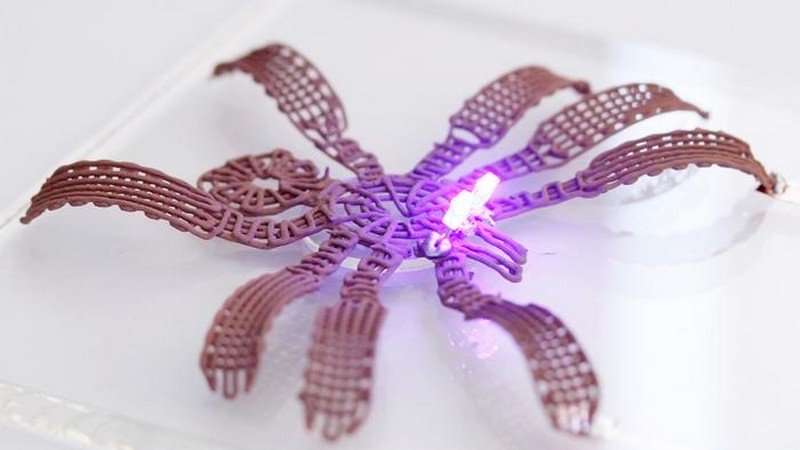
Researchers have achieved a significant breakthrough in 3D printing with the development of a metallic gel that can be used to print solid objects at room temperature. This ground-breaking technology enables the production of three-dimensional metal objects in a single step, potentially revolutionizing the manufacturing industry. How does the metallic gel enable the printing of three-dimensional metal objects at room temperature, what advantages does the gel offer in terms of conductivity compared to other 3D printing materials, and how can the controlled structural changes induced by heat during the drying process be utilized in practical applications?
Open-Source Hardware News
Picopad Is An Open-Source Game Console With A Raspberry Pi RP2040 Microcontroller
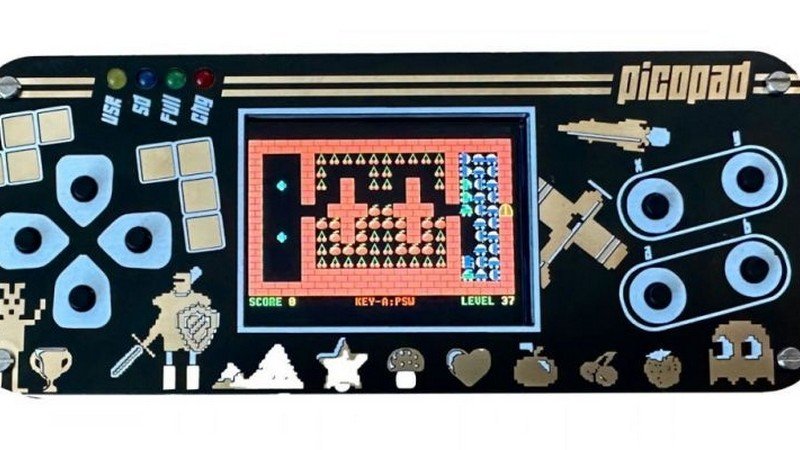

The Picopad is a compact game console that offers a 2-inch IPS LCD display with a resolution of 320 x 240 pixels and a set of eight buttons, including four functioning as a pseudo-direction pad. Powered by a Raspberry Pi Pico with an RP2040 microcontroller, this open-source device brings classic arcade games like PAC-MAN, Centipede, Space Invaders, Tetris, and even DOOM to life. It is available for purchase in the Czech Republic for approximately $40 and comes with accessible hardware schematics, software, and SDK files on GitHub. How does the RP2040 microcontroller in the Picopad provide sufficient processing power for running classic and newer games, what are the advantages and limitations of the Picopad’s unique design with stacked circuit boards and the absence of a dedicated case, and how do the Picopad models with and without wireless support differ in terms of functionality?
