

In this week of engineering, we have seen multiple developments in plastic waste management including start-ups looking to track waste while researchers continue to explore the use of enzymes to break down plastic in landfills. Looking up to the sky, NASA has developed a new 3D printed alloy that is 1000 times stronger than previous prints, and X-BOW is looking to create disposable 3D printed rocket parts with the help of a $27 million funding round. And RISC-V continues to make strong advances with the Ministry of Electronics and IT in India looking to secure a premier membership spot in the RISC-V International organisation.
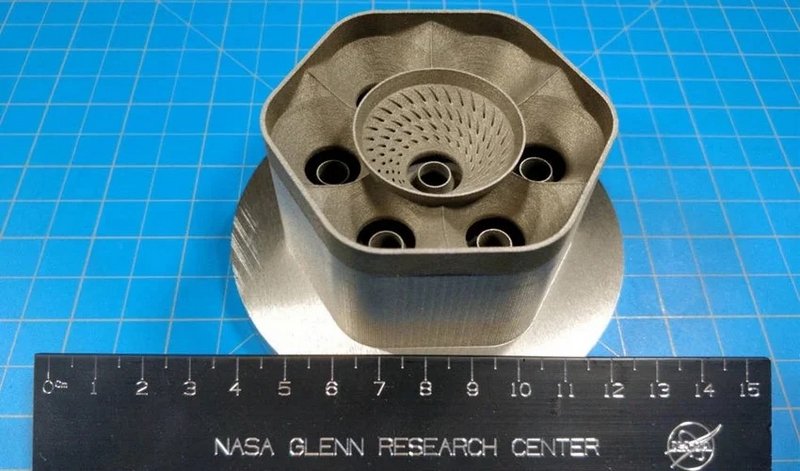
NASA engineers develop new 3D printed metal alloy with 1000x more strength

Alloys play a crucial role in high-tech industries, especially those in aerospace thanks to their unique qualities whether it is high-temperature resistance, high tensile strength, or the ability to undergo deformation without damage. Recently, NASA researchers have pushed the limits of 3D printed parts with the creation of a new alloy that is 1000 times stronger than previously made 3D printed alloys. How would 3D printed parts benefit NASA and other space-related missions, what challenges did the researchers face, and could this alloy be viable for space missions?
Hardware Business News
X-BOW Systems raises $27 million for advancing 3D printed rocket technologies

3D printing has made itself very famous in the field of rapid prototyping, but some are looking at the technology for use in disposable parts. Recently, rocket engine company X-BOW has been awarded $27 million in Series A funding to develop the next generation of 3D printed rocket engines in partnership with Lockheed Martin. Who is X-BOW, what will the funds be used for, and could 3D printing be the solution for future rocket engines?
Smart sensor collaboration secures $5 million for targeted intelligent care

As society continues to age, ensuring proper care for the most vulnerable is an increasingly difficult challenge. However, the use of sensors and IoT technologies can help to ease this pressure by monitoring those who are vulnerable and then sending help to those who most need it. Recognising the serious advantage of IoT technologies in care, the NSW Government in Australia has announced a $5 million fund that will target both small and medium-sized businesses to tackle the challenges of remote care. How will the funds be distributed, how can IoT sensors be used in healthcare, and what businesses can apply for funds?
DJI suspends business operations in Russia over Ukraine war

The Russian-Ukraine war has been a horrific tragedy for those living in Ukraine, but the strong response of governments and businesses around the world has shown almost unanimous support for Ukraine. However, DJI has recently announced that it will be suspending business operations in Russia over its use of their drone technology in active war zones. How are cheap drones decimating modern military technologies, what involvement does DJI play in this war, and why is China nervous to get involved?
India moving into RISC-V architecture – Another win for RISC-V
There is increasingly strong evidence that RISC-V will become a major CPU architecture of the future if proprietary alternatives do not change their business strategies. Recognising the strength of RISC-V, the Ministry of Electronics and IT in India has announced plans to become a premier member in the RISC-V International organisation. What advantages does RISC-V have over other processor technologies, why would the Ministry of Electronics and IT in India want to join, and will RISC-V overtake ARM in the future?
Startup receives funding of $100,000 from the US EPA to track plastic

Plastic waste is an ever-growing problem in modern society no thanks to its inability to decompose, become potentially toxic when ingested, and extremely cheap nature. One startup in the US thinks it has a solution that will allow for plastic waste to be traced, and the EPA has now provided a grant of $100,000 to test the idea out. Where does plastic waste come from, what does the new startup intend to do, and how do quantum databases get involved?
Hardware Engineering News
Ransomware becoming a growing concern for digital infrastructure and governments
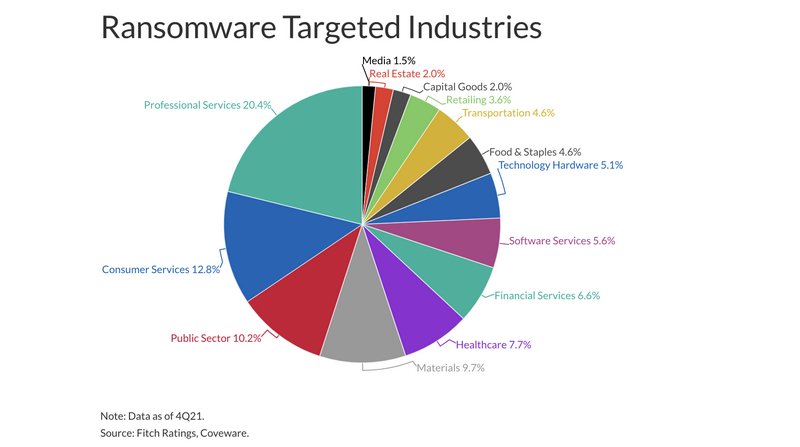
Viruses and trojans were the main threats of the past, and while they were a very serious problem, you could be sure that personal files would rarely be lost. However, the growing rise of ransomware has created a digital environment where files can easily be encrypted and lost forever, and this is now even threatening governments and financial systems. In this article, learn about the true scale of ransomware attacks, what they typically target, and the industries most affected.
How 3D printing can help to fight against the semiconductor shortage
Ever since the widespread introduction of 3D printing a decade ago, engineers around the world are rushing to use it in almost any application you can think of. Recently, NASDAQ published an article describing how the use of 3D printing technology may be able to help the semiconductor shortage with the ability to fabricate custom parts for new foundry equipment. What challenges does the semiconductor industry face, how could 3D printing help, and how realistic is the use of 3D printed parts in the semiconductor industry?
Technologies Next Wave – How do Americans feel about new technologies?

As new technologies are introduced, those who cannot keep up are often left behind, and this is one of the biggest drawbacks of the recent technological boom due to computers and the internet. Recently, a YouGov poll was done on 16 different emerging technologies including AR, VR, and AI to see how much exposure new technologies have had, and how the public feels about it. What are these new technologies, what does the public think, and which of those technologies will be beneficial to society?
Hardware R&D News
Researchers develop enzyme with the ability to decompose plastic waste

Despite plastic being a widely recyclable material, large amounts continue to fill up landfills. As plastic doesn’t decompose quickly (if at all), any plastic that goes into a landfill takes up space that could otherwise be used for more important waste. In response to this challenge, researchers have recently developed an enzyme that can break down plastics in landfills. What challenges do landfills face, how did the researchers develop the enzyme, and are enzymes the future solution to plastic waste?
