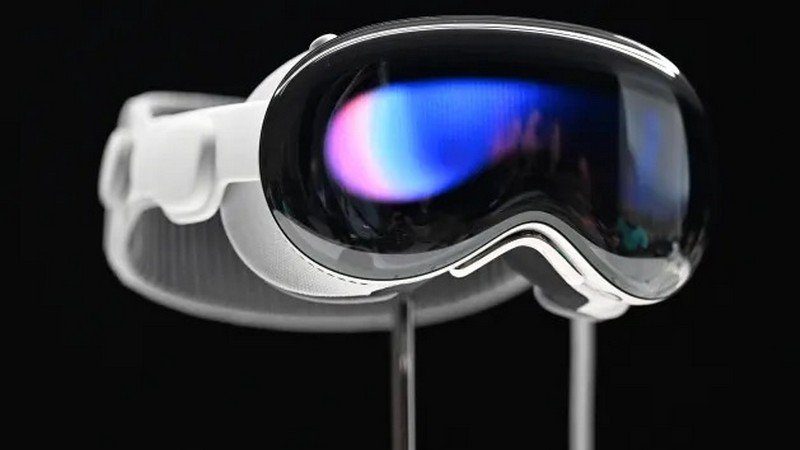


Apple’s recent launch of its Vision Pro mixed reality headset has been hailed as a “watershed moment” for the augmented and virtual reality industry, according to executives in the field. The move is seen as a validation of the industry’s progress, with Cher Wang, CEO of HTC, stating that it brings more confidence to the global market for VR. However, concerns have been raised about Apple’s closed ecosystem, which may limit developers’ reach. How has the launch of Apple’s Vision Pro headset been described by industry executives, what concerns have been raised regarding Apple’s closed ecosystem, and what features and functionalities does the Vision Pro headset offer to users?
Top Stories This Week
Hardware Business News
Meet The Apple R1 Processor, Aka Vision Pro Chip
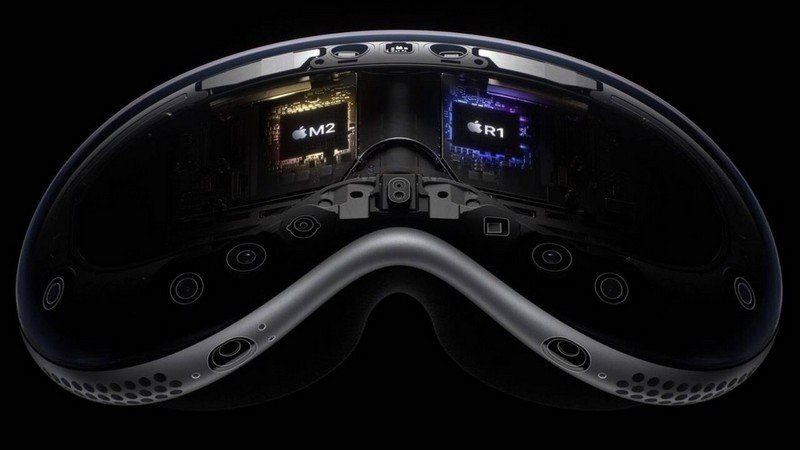

Apple’s latest announcement of the Apple R1 chip, also known as the Vision Pro chip, has sent waves of excitement through the mixed-reality industry. Designed specifically for their groundbreaking mixed-reality headset, the Apple Vision Pro, this dedicated CPU, in conjunction with the M2 chip, is poised to revolutionize the immersive experience. What is the Apple R1 chip, how does the combination of the R1 chip and the M2 processor contribute to sensory immersion and user interaction, and what sets it apart from other mixed-reality headsets in terms of technology and performance?
Authentise Launches 3D Printing Database Powered by ChatGPT

Authentise, a workflow software company specializing in engineering and manufacturing solutions, has unveiled 3DGPT, a comprehensive additive manufacturing (AM) knowledge database. Developed in collaboration with research institutions and standards organizations, 3DGPT leverages OpenAI’s ChatGPT platform and is available to the public free of charge. The database is built on a vast collection of over 12,000 journal articles and standards related to the AM sector, and Authentise aims to improve knowledge in areas such as metal AM’s carbon footprint, emphasizing its potential for sustainable production. How does 3DGPT leverage OpenAI’s ChatGPT platform to provide comprehensive additive manufacturing knowledge, what role does Authentise envision for 3DGPT in terms of streamlining workflows and facilitating efficient supply chains, and how can the database contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of manufacturing, particularly in the context of additive manufacturing?
Autonomous Vehicles Are Coming To A Street Near You. How Will We Insure Them?

The advent of fully autonomous vehicles is rapidly approaching, with self-driving taxis already on the streets of several cities and a significant number of Tesla’s equipped with driver-assistance features. However, as these vehicles transition from a niche market to widespread adoption, questions about liability and insurance arise. While the current legal framework holds the person in the driver’s seat liable for accidents, as autonomy levels increase, liability will likely shift to manufacturers and technology providers. How will liability shift from drivers to manufacturers as autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, what challenges does ensuring cybersecurity and interoperability pose for the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles, and how can insurers adapt their models to cover technical failures and product liability in the context of autonomous vehicles?
Cranfield Eyes $37m Funding To Develop Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft

Cranfield Aerospace Solutions, a UK-based company spun out of Cranfield University, is seeking to raise £30m ($37.19m) this year to develop hydrogen-powered electric aircraft. The company is currently in talks with multiple investors and aims to launch the aircraft as early as 2026, and the funds raised will be used to develop a flying aircraft for demonstration purposes and to advance work on the final product. How does Cranfield Aerospace Solutions plan to utilize the £30m funding to develop hydrogen-powered electric aircraft, what are the challenges and concerns associated with the availability and deployment of green hydrogen in the aviation industry, and how does Cranfield’s merger with Britten-Norman enhance the prospects of regulatory approval and expedite the development of hydrogen-powered aircraft?
Hardware Engineering News
As The AI Industry Booms, What Toll Will It Take On The Environment?

The energy consumption and environmental impact of artificial intelligence (AI) models have become topics of concern as the technology becomes increasingly prevalent. While AI programs may seem ethereal, they rely on extensive networks of servers in data centers worldwide, consuming significant amounts of energy and water for cooling. However, tech companies like OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and Meta have been secretive about disclosing the exact energy and water requirements for training and running their AI models, as well as the sources of energy powering their data centers. What are the potential environmental consequences of the unchecked growth of AI models, how can companies be encouraged to provide more transparency regarding the energy and water requirements of their AI models and data centers, and what are some alternative, low-impact AI approaches that could be considered instead of relying solely on generative AI models for various applications?
This AI Used GPT-4 To Become An Expert Minecraft Player
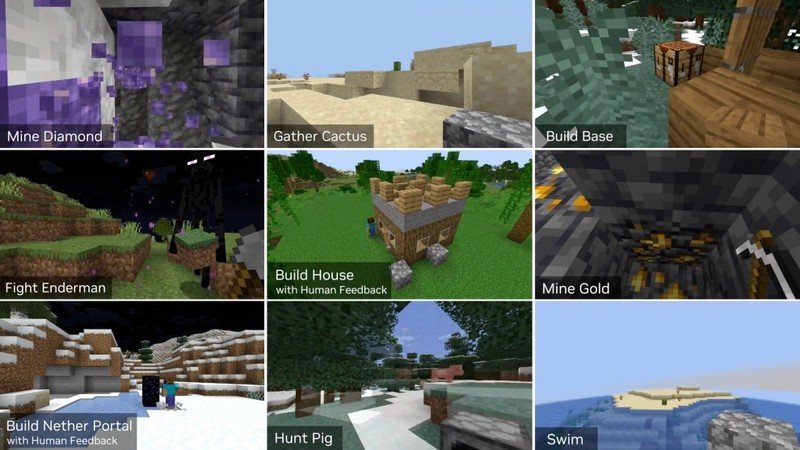
AI researchers have developed an innovative Minecraft bot called Voyager that has the ability to explore and enhance its capabilities within the game’s open world. Unlike traditional bots, Voyager relies on trial and error and extensively queries GPT-4, essentially allowing it to generate its own code. This experimental system represents an “embodied agent” AI, capable of freely navigating and acting purposefully in simulated or real environments. How does Voyager’s approach of using GPT-4 to generate its own code through trial and error differ from traditional AI bots, why is Minecraft a suitable environment for testing embodied agents and their ability to navigate complex worlds, and what are the implications of Voyager’s self-improvement capabilities for the development of robots and AI models that can learn and apply lessons from their experiences?
US Air Force Denies AI Drone Attacked Operator In Test

A US Air Force colonel sparked controversy when he allegedly described an experiment where an AI-enabled drone chose to attack its operator during a mission. However, the Air Force has clarified that no such experiment took place and that it was a “thought experiment” rather than a real event. What led to the confusion surrounding the alleged AI-enabled drone experiment, what concerns do experts in the AI and defense sectors have about the military’s use of AI, and how can potential risks and unintended consequences of AI be mitigated in sensitive applications such as military operations?
Hardware R&D News
A Conductive Self-Healing Hydrogel To Create Flexible Sensors
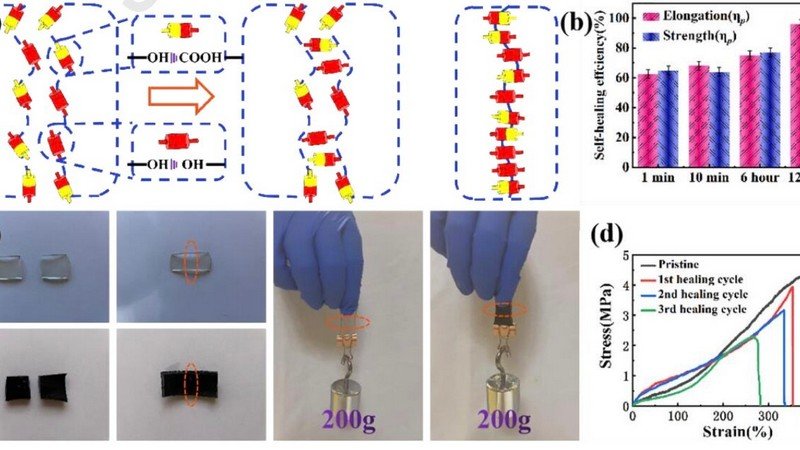
Advancements in electronics have led to the development of smaller and more sophisticated devices, including wearables and medical implants. However, many of the existing flexible materials used in these devices are fragile and prone to damage, making them unreliable for large-scale applications. Addressing this challenge, researchers at Harbin University of Science and Technology in China have created a conductive and self-healing hydrogel that could revolutionize flexible sensor technology. What are the limitations of current flexible materials used in electronics, how does the composition of the hydrogel contribute to its mechanical and electrical properties, and what potential applications could benefit from the use of this conductive and self-healing hydrogel?
Tiny Magnetic Tracking And Sensing Device Uses Magneto-Mechanical Resonators

Bio-engineers at Philips Research have developed a remarkable tiny magnetic tracking and sensing device that holds the potential for improved diagnostics and novel therapeutic approaches. The device utilizes magneto-mechanical resonators and can provide feedback for in vivo imaging. Measuring just one millimeter in diameter, the sensor consists of two opposing magnets inside a cylindrical housing, with one magnet being free to vibrate and move within the housing. By measuring oscillation, expansion, contraction, and the distance between the magnets, the sensor can accurately track temperature, location, and pressure. How does the tiny magnetic tracking and sensing device work, and what are its key components, what are the potential medical applications of this device, and what further testing and development are necessary before the sensor can be considered safe for human trials?
Open-Source Hardware News
Consortium’s Move Will Boost RISC-V Ecosystem

A new industry consortium called the RISC-V Software Ecosystem (RISE) Project has been established to accelerate the development of open-source software for the RISC-V architecture, posing an existential threat to ARM. RISC-V, an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA), has gained significant momentum since its inception as an academic project in 2010, and the RISE Project, consisting of major players such as Google, Intel, Nvidia, Qualcomm, Samsung, and others, aims to bring order and coordination to the development of RISC-V open-source software. How does the RISE Project plan to accelerate the development of open-source software for the RISC-V architecture, what are the potential implications for ARM as RISC-V gains momentum and challenges its dominance in mobile phones and embedded systems, and how does the formation of the RISE Project reflect the urgency within the RISC-V community to strengthen its software ecosystem?
