

Google has taken a proactive step in enhancing its cybersecurity measures by introducing a new pilot program that restricts internet access on certain desktop PCs used by employees. According to CNBC, the initiative aims to reduce the risk of cyberattacks targeting Googlers, who are frequently targeted by malicious actors. The program will involve disabling internet access on select desktops, with exceptions made for internal web-based tools and Google-owned websites like Google Drive and Gmail. While initially intended for over 2,500 employees, Google revised the pilot based on feedback, allowing employees to opt-out and opening it up to volunteers. What is the primary purpose of Google’s pilot program that restricts internet access on certain desktop PCs used by employees, how did Google respond to employee feedback regarding the pilot program’s implementation, and what potential risks does this measure aim to mitigate in terms of cybersecurity?
Top Stories This Week
Hardware Business News
US Government Launches Certification For Smart Devices

The Biden-Harris Administration has unveiled the “U.S. Cyber Trust Mark” program, aiming to raise cybersecurity standards for smart devices. Supported by major companies like Amazon and Google, the program will provide a distinct logo for products meeting established cybersecurity criteria, and the FCC plans to seek public comment and roll out the program in 2024. NIST will define cybersecurity requirements for consumer-grade routers, and the Department of Energy will research smart grid cybersecurity. What is the U.S. Cyber Trust Mark program, and what does it aim to achieve for smart devices, which major companies have committed to the program, and how will they enhance cybersecurity, and how will the program leverage QR codes and NIST guidelines to provide cybersecurity information to consumers?
Openreach On Concerns Over Lead Poisoning From Old UK Cables

The Wall Street Journal’s alarming report on lead-insulated telecoms cables causing soil and water contamination has raised concerns about potential risks. The report found lead present in the soil at multiple locations beyond safe levels determined by the EPA. In the UK, Openreach (BT) clarifies that they no longer install lead-sheathed cables but still manage legacy cables in underground ducts. The risk of lead poisoning from such cables appears to be low, but further research may be needed. What is the focus of the alarming report by The Wall Street Journal, how has Openreach (BT) addressed the issue of lead-sheathed cables in the UK, and what further research is needed to assess the potential public health risks?
Next Apple Watch Ultra May Contain 3D-Printed Parts

Apple is reportedly exploring the use of 3D-printed components for the next version of the Apple Watch, according to analyst Ming-Chi Kuo. The move to 3D printing could potentially lead to improved production times and reduced costs for mechanical parts in the Apple Watch Ultra. IPG Photonics is said to be the exclusive supplier of the laser components used in Apple’s 3D printers, while Farsoon and BLT are the printer suppliers. The launch for the next-gen Apple Watch Ultra is rumored to be in the second half of 2023, with possible enhancements such as a larger screen and a Micro LED display. What benefits does Apple hope to achieve by using 3D-printed components for the Apple Watch Ultra, who are the key suppliers involved in Apple’s 3D printing process, and what are some of the rumored enhancements expected in the next-generation Apple Watch Ultra?
US Expected To Get Around China’s Export Controls On Gallium

The Biden administration has expressed firm opposition to Beijing’s new restrictions on the export of germanium and gallium, crucial materials for semiconductors, communications equipment, and solar panels. As tensions between the two global powers escalate, the US Commerce Department advocates diversifying supply chains and engaging with allies to build resilience. China’s dominant role as a producer of these elements presents potential challenges for critical mineral supply chains. How significant are germanium and gallium in semiconductor and communication equipment manufacturing, how does the Biden administration plan to respond to China’s export restrictions on strategic materials, and with tensions rising between the US and China, how are US allies responding to Beijing’s export controls?
Hardware Engineering News
Can Australia Manufacture The Billion Solar Panels It Needs To Be A Renewable Superpower?

The Australian government is funding a groundbreaking study aimed at reviving the country’s solar panel manufacturing industry. The study, supported by a grant from the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, will explore how Australia can set up its own solar panel manufacturing sector to meet its renewable energy ambitions. While Australia is a leader in solar research, its position as a manufacturer was lost to China in 2012, with China now dominating global solar panel manufacturing. The study aims to identify the steps needed to create a robust domestic market for locally manufactured panels and address technical, commercial, regulatory, and social license challenges. Why is the Australian government investing in the Silicon to Solar study, how does Australia’s solar research expertise play a role in the development of the domestic manufacturing sector, and what strategies and government support will be crucial for Australia to compete with China’s mature manufacturing industry and establish a reliable and sustainable supply chain for solar panels?
Bending The Power: The Future Of Flexible Lithium-Ion Batteries

Today, researchers are exploring flexible batteries as crucial energy storage for future flexible applications, particularly in wearable electronics. These batteries address safety concerns of traditional lithium-ion batteries, making them essential for powering flexible displays, healthcare devices, and e-textiles. Key materials like carbon nanotubes and graphene contribute to their high energy density and mechanical flexibility, while innovative structural designs enable bending, twisting, and stretching properties. Despite challenges, further research aims to establish these batteries as a vital component for powering the future of flexible electronics. What are the main advantages of flexible solid-state batteries over conventional rechargeable lithium-ion batteries in the context of flexible and wearable electronics, what materials and innovative structures are central to the performance and mechanical flexibility of flexible lithium-ion batteries, how do the high-energy flexible solid-state lithium-ion batteries that operate at room temperature overcome some of the challenges associated with wearable applications?
GGtag Is A Reusable, Reprogrammable ePaper-Based Badge With RFID
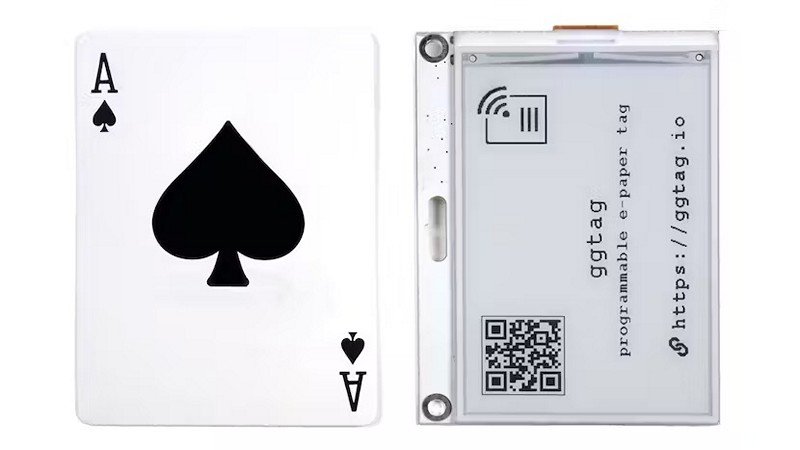

Eurolan, a networking equipment company, has introduced GGtag, an innovative electronic option that combines plastic identification badges and RFID-based access cards into a reprogrammable ePaper badge with programmable RFID. The GGtag features a 3.52″ ePaper display, driven by an RP2040 microcontroller, and a Microchip ATtiny85 microcontroller emulating RFID tags. It can be programmed via USB or a unique audio-based method using a web app and sound, making it ideal for shared workspaces and reusable conference badges. The open-source design files and web-based interface allow users to customize the e-paper badge with text, icons, and images for easy programming. The Crowd Supply campaign for GGtag is in the preliminary stage, with interested individuals invited to join the mailing list for updates on the campaign’s launch. What is the main feature of the GGtag electronic badge, what are the two methods available for programming the GGtag, and how can users customize the e-paper badge?
Hardware R&D News
New Skin-Like Sensors Fit Almost Everywhere
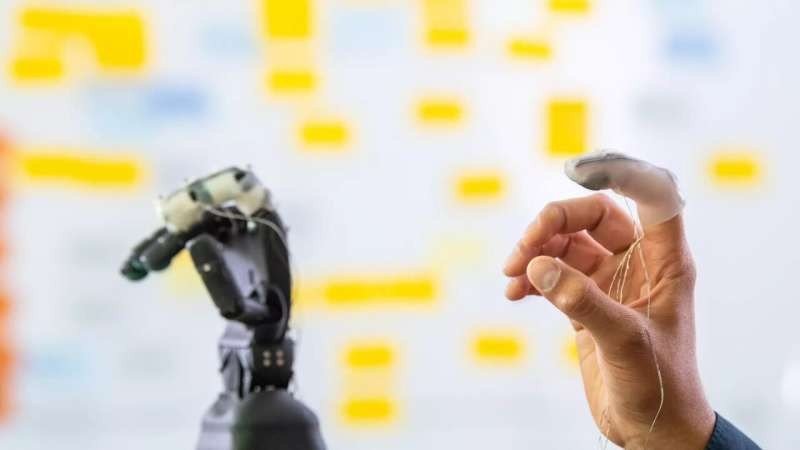

Researchers from the Munich Institute of Robotics and Machine Intelligence (MIRMI) at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have made a significant breakthrough in the field of soft sensors. They have developed an automated process for creating soft measurement cells that can be attached to almost any object, holding potential applications in robotics and prosthetics. Unlike traditional sensors, these soft sensors can be customized and attached to objects of various shapes and sizes, providing valuable feedback on interactions with the environment. The researchers’ work has opened up new possibilities for advanced haptic sensing in artificial intelligence and has the potential to revolutionize industries such as robotics, prosthetics, and human-machine interactions. What are soft sensors, how does the new framework for soft sensors differ from traditional sensors in terms of customization and attachment, and what potential applications and benefits do soft, skin-like sensors bring to industries like robotics and prosthetics?
Jellyfish-Like Robots Could One Day Clean Up The World’s Oceans
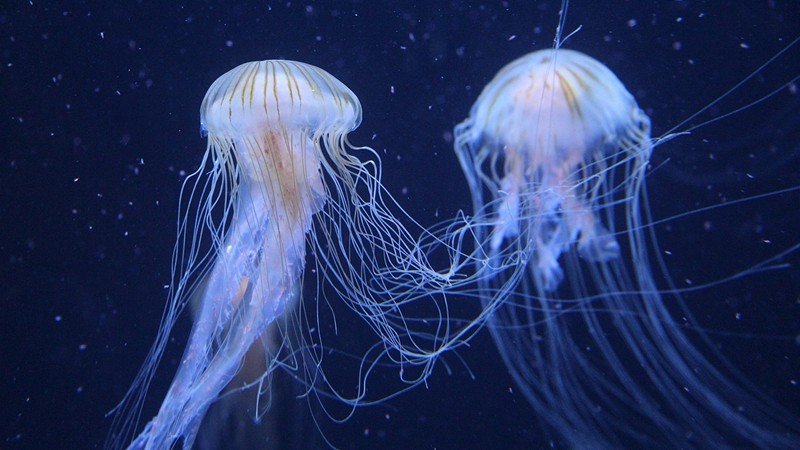

Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems have developed a jellyfish-inspired underwater robot called Jellyfish-Bot that could play a crucial role in combatting ocean pollution. The robot is designed to be versatile, energy-efficient, and nearly noise-free, making it ideal for delicate environments such as coral reefs. Using electrohydraulic actuators and air cushions, the robot mimics the graceful movements of a jellyfish, circulating water around its body to collect objects like waste particles and fragile biological samples. The Jellyfish-Bot’s ability to move without physical contact and its low input power make it a promising tool for cleaning up oceans and preserving marine life. How does the design of the Jellyfish-Bot make it suitable for exploring and cleaning delicate ecosystems like coral reefs, what are the potential applications of the Jellyfish-Bot in cleaning up marine litter and assisting with delicate tasks such as collecting biological samples, and what are the challenges and future goals the scientists aim to address in developing the Jellyfish-Bot, particularly with regards to creating wireless robots for ocean exploration?
Open-Source Hardware News
How China Is Building An Open National Chip Plan Around RISC-V
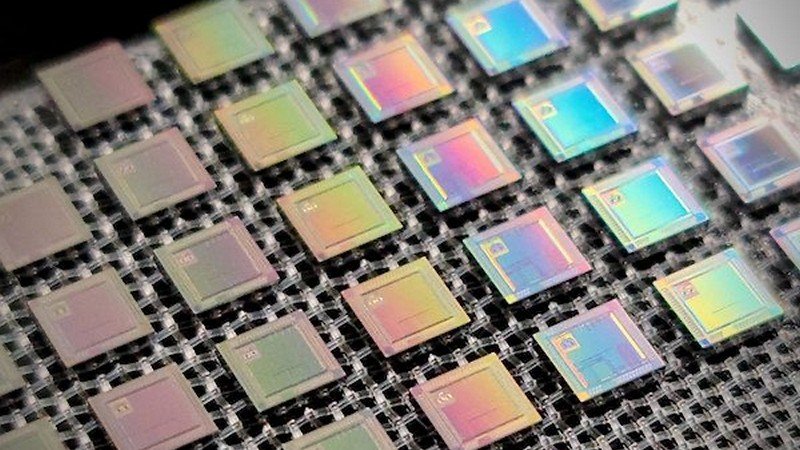
China’s push to reduce reliance on Western chip technology is focusing on homegrown chips built using the open RISC-V architecture. RISC-V offers a free-to-license API blueprint to build chips, and the Chinese government has shown significant interest in funding RISC-V initiatives this year. Meanwhile, the U.S. is also involved in RISC-V development but has faced setbacks in the private sector. What are the main reasons for China’s interest in developing homegrown chips using the RISC-V architecture, how is China working towards creating a full open-source chip ecosystem based on the RISC-V architecture, and how has the U.S. semiconductor industry been impacted by the RISC-V development and the shortage of talent in the sector?
